Movie Rating Predictor Service
This project is a serverless ML system that predicts IMDb ratings for movies using a dynamic dataset from Kaggle.
Overview
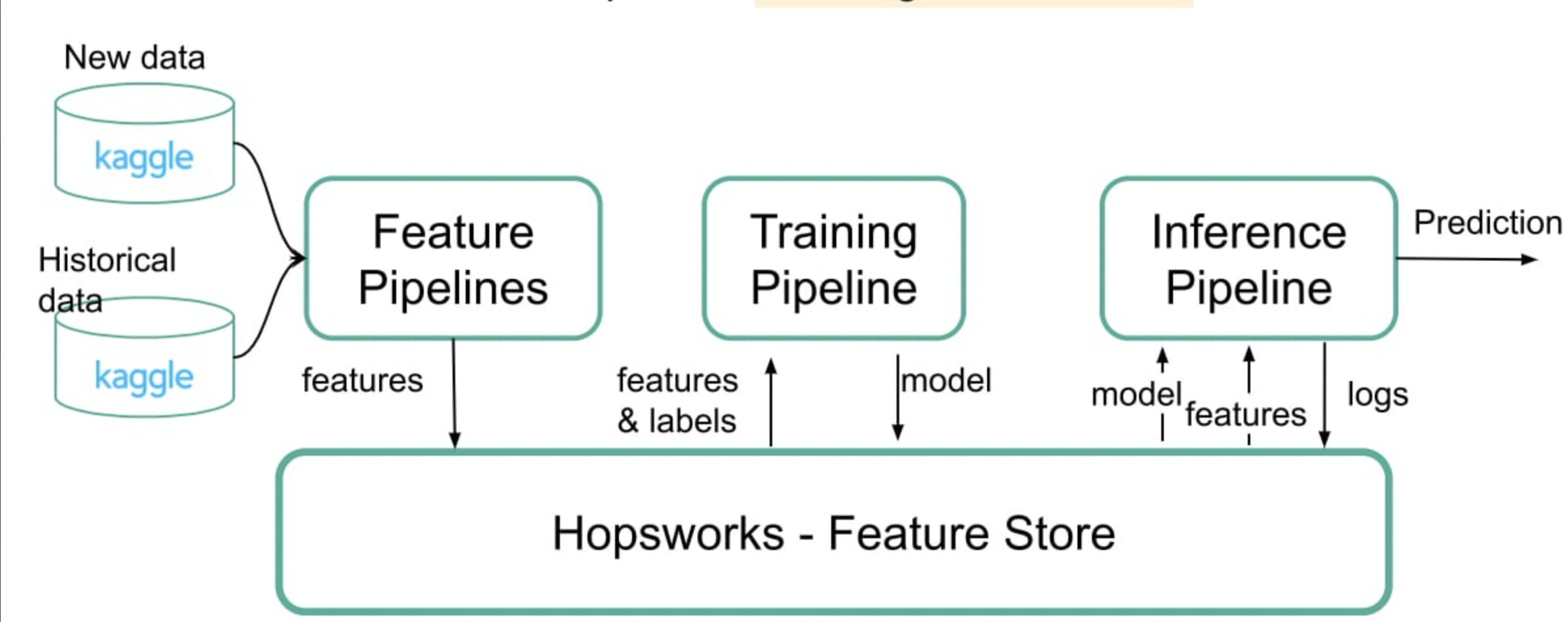
This project is a serverless ML system that predicts IMDb ratings for movies using a dynamic dataset from Kaggle. The system comprises four main pipelines:
- Historical Data Pipeline: Backfills the feature store with historical data.
- Feature Pipeline: Handles daily data updates.
- Training Pipeline: Trains the machine learning model.
- Inference Pipeline: Uses the trained model to predict ratings for new movies.
A user interface (UI) is available for monitoring predictions. The website allows users to explore different movies, view predicted ratings, and navigate to the IMDb page of a selected movie to see its actual IMDb rating.
Key technologies used include Hopsworks for the feature store and GitHub Actions for automating daily workflows and pipeline execution.
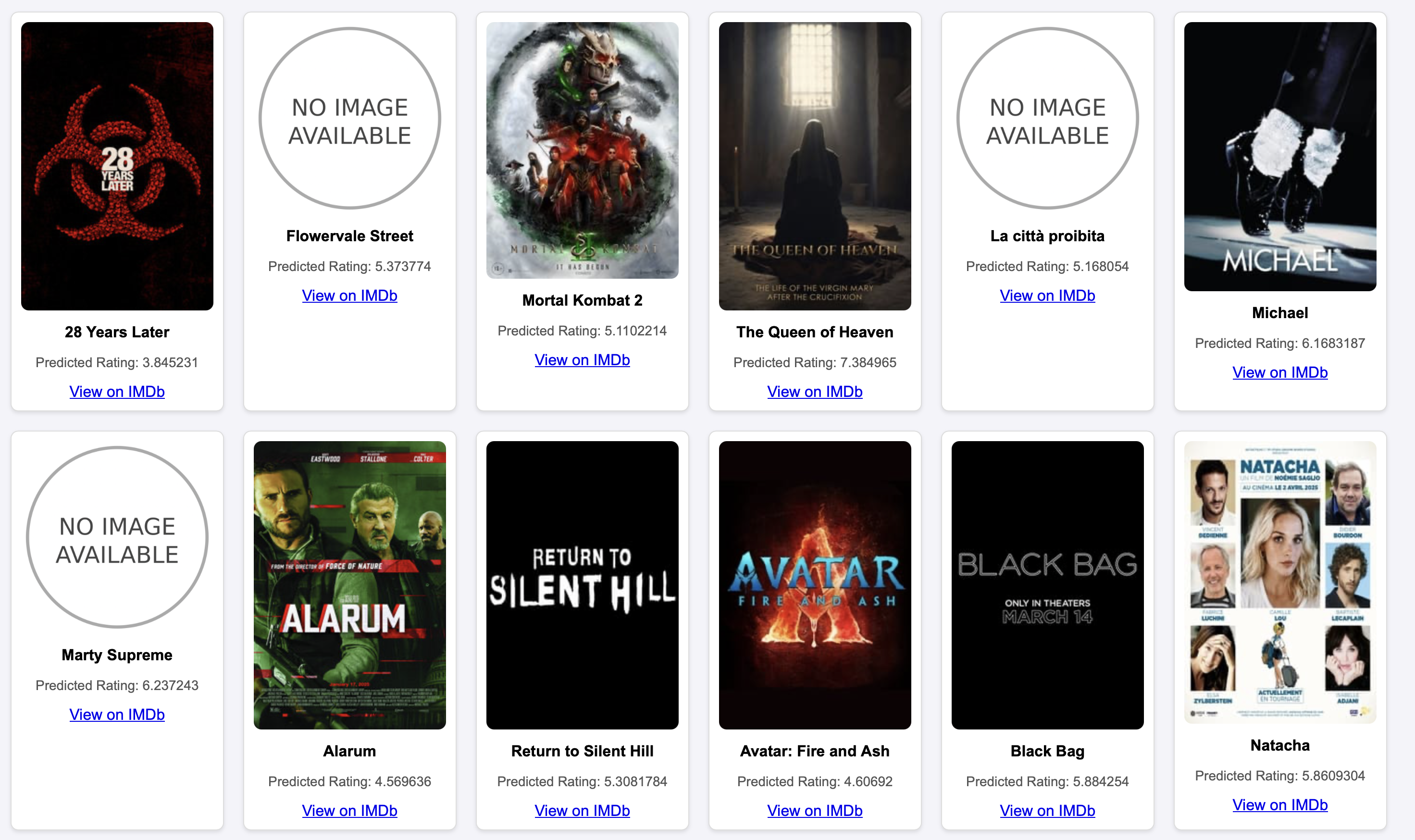
The website is available at Movie Rating Predictor.
The repository is available at Movie Rating Repository.
We can see the predicted ratings for 20 newly updated movies. If we click on the movie poster, we will be redirected to the IMDb page of the movie to see the actual IMDb rating.
Dataset
The dataset used is from Kaggle, containing the complete movie list from The Movie Database (TMDB) along with IMDb information. It includes 28 columns, such as:
-
vote_average,vote_count,status,release_date,revenue,runtime,budget -
imdb_rating,imdb_votes,original_language,overview,popularity,tagline -
genres,production_companies,production_countries,cast,producers,directors,writers
The dataset is updated daily, ensuring its dynamic nature.
Methodology
Historical Backfilling
Historical data backfilling was done by filtering movies with the status set to “Released,” ensuring that IMDb ratings were available for training. Missing data columns were dropped, and data cleaning was performed.
Feature Engineering
Features vote_average and popularity were removed since they can be seen as measures of the movie’s rating, which would bias the model. The target to predict was imdb_rating, making vote_count also irrelevant. The release_date column was converted to release_year, grouping movies by year.
New features were derived:
- First values from
producers,cast, andproduction_companiescolumns were extracted intofirst_producer,first_actor, andfirst_companyand label-encoded. - The
genrescolumn was one-hot encoded, creating a separate feature group that was merged in the training pipeline.
Including the categorical feature original_language improved model performance, leading to lower MSE and higher R-squared values.
Final features used for training included:
-
budget,runtime,release_year,imdb_votes -
first_producer,first_actor,first_company,original_language - One-hot encoded
genres(19 unique genres)
This resulted in a total of 27 features.
Models
The following models were compared:
- XGB Regressor
- Random Forest Regression
- Linear Regression
- SVR
- Decision Tree Regressor
The XGB Regressor emerged as the best-performing model, with an MSE of 0.54 and an R-squared value of 0.58. The Random Forest Regressor performed closely, offering simplicity and adaptability for varying dataset sizes.
Inference Pipeline
For the inference pipeline, predictions were made for:
- Newly released movies.
- Movies in “Post Production” status (with estimated
imdb_votesof 400 and average runtime of 124 minutes).
The website displays both predicted and actual IMDb ratings for 20 newly updated movies.
Results
The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the XGB Regressor. Below is a sample comparison of predicted and actual IMDb ratings:
| Predicted | Actual |
|---|---|
| 5.857948 | 7.1 |
| 6.3983464 | 6.3 |
| 5.2628407 | 6.1 |
| 4.411699 | 4.2 |
| 5.9354286 | 5.9 |
| 6.1494517 | 6.1 |
| 4.789273 | 4.4 |
| 4.68718 | 4.2 |
| 4.7766104 | 6.6 |
| 6.090134 | 6.3 |
Some predictions are close to the actual ratings, while others show expected variance, reflecting the complexity of factors influencing IMDb ratings.